LONDON (Realist English). The Guardian reports that the UK and India have agreed on 90% of the terms of a long-awaited free trade agreement (FTA), according to British businesses briefed this week by government negotiators. The deal, hailed as one of the most significant post-Brexit trade opportunities, could be finalised later this year.
A British government source confirmed that mobility provisions — a sticking point over visas for Indian professionals — have been «largely resolved». “We are nearly there,” the source said, noting that final steps now hinge on political will from both sides.
Negotiators revealed that the remaining issues involve tariffs and regulations affecting whisky, cars, and pharmaceuticals. The FTA could significantly cut duties on UK exports of Scotch whisky and automobiles, bolstering sectors hit by protectionist measures from the US.
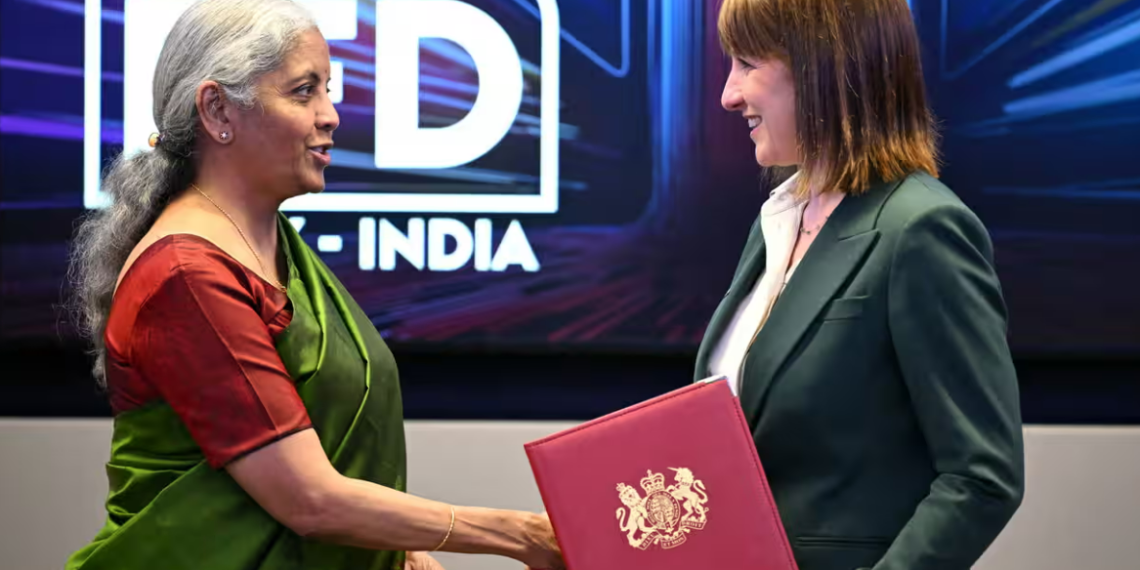
The update came ahead of a series of high-level meetings in London between UK officials and Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman. She met with Shadow Chancellor Rachel Reeves, Labour leader Keir Starmer, and Trade Secretary Jonathan Reynolds. Reeves later stressed the importance of accelerating trade deals to “kickstart economic growth”.
Parallel talks are also underway on a bilateral investment treaty, a key demand of the UK financial sector that would provide legal protections for cross-border investments.
India, facing rising global economic uncertainty, is actively seeking new bilateral trade partnerships. Speaking at the Indian High Commission in London, Sitharaman said the UK deal was a priority and expressed optimism: “There is a great sense of positivity and dedication to conclude it soon.”
During her visit, British ministers unveiled £128m in new export deals and investment commitments with India. Industry leaders welcomed the momentum. Keshav Murugesh, CEO of tech firm WNS, said a deal would “fuel innovation and generate high-skilled jobs” in both countries.
However, one unresolved issue remains politically sensitive: India’s request to be excluded from the UK’s upcoming carbon border tax, a measure designed to protect UK industries like steel from cheaper, high-emissions imports. London has not yet committed to an exemption.
Formal negotiations for the UK–India FTA began in January 2022. Despite repeated efforts by Conservative governments to fast-track the deal, talks have dragged on due to complex trade-offs between services, goods, and environmental standards.
If concluded, the UK–India deal would mark a major post-Brexit milestone, giving British exporters improved access to a 1.4 billion-strong market and tightening ties with one of Asia’s fastest-growing economies. But any concessions on climate-related taxes or market protections could trigger domestic political backlash. Finalising the deal will test the UK’s ability to balance strategic trade goals with industrial and environmental interests.